Stay ahead: Updates for UFS Explorer you need to know about in 2024
10.12.2024
To remain useful in today’s fast-paced world of storage technologies, data recovery tools must keep up with constantly advancing challenges. And UFS Explorer has always responded to them with timely updates. Such updates are meant not only to improve the existing product’s functionality, but also introduce innovative features that simplify the recovery process or make it more effective. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the major updates released since the beginning of this year, demonstrating how different editions of UFS Explorer are evolving to better serve the needs of data recovery professionals and ordinary users alike.
A brief overview of what's new in each version of the products is also provided in their respective changelogs:
- UFS Explorer Standard Recovery
- UFS Explorer RAID Recovery
- UFS Explorer Network RAID
- UFS Explorer Professional Recovery
- UFS Explorer Technician
All editions of UFS Explorer
Enhanced disk imaging
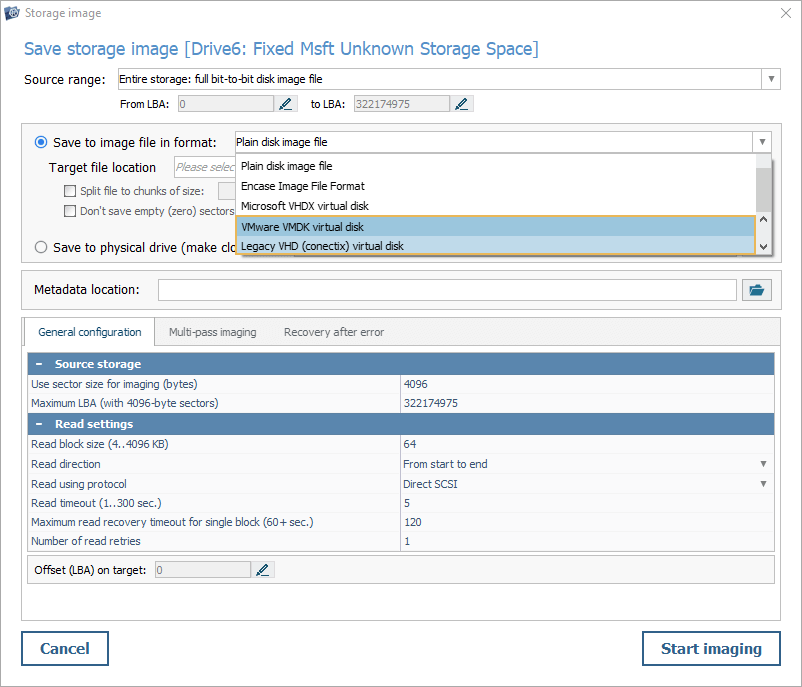
The disk imaging tool integrated into each edition of UFS Explorer has been expanded with several new output formats. To begin with, now it allows saving files as VMDK virtual disks, a common format used by the VMware virtualization platform. Therefore, disk images produced by it can be directly compatible with VMware products, without the need for any additional conversion. Meanwhile, the size limitation for such files has been increased to 128 exabytes, which greatly exceeds VMware's default 8 TB limit. Moreover, it is possible to divide large virtual disks into smaller segments by using VMware's native chunking mechanism, known as "chunked" VMDK. Apart from VMware's VMDK, the imager presently supports VHD, a legacy virtual disk format that is still widely employed in older virtual environments, especially those relying on Microsoft Hyper-V.
The tool has also become more helpful for imaging enterprise storage systems, particularly Storage Area Networks. The latter often consist of numerous drives, each assigned with a unique Device ID (WWN) that is essential for proper SAN configuration and further management. UFS Explorer is currently capable of reading the WWN identifiers of SATA and SAS drives, and preserves this information in their disk images saved in the SDLSP format. The automatic capture of WWNs, along with other essential details, allows maintaining the identity of the drive components and greatly simplifies their subsequent recognition. This also makes it much easier to reproduce the original SAN layout upon necessity.
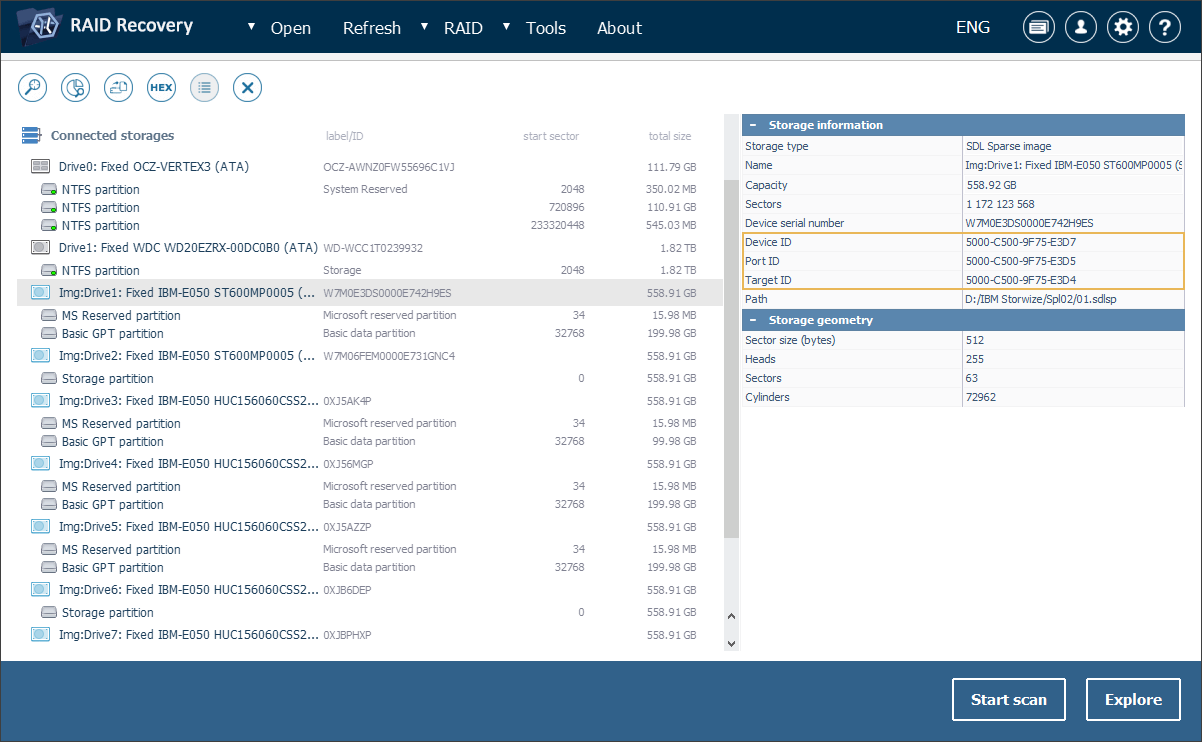
When the imaged drive is reconnected and receives a different device path, for example, after switching SATA ports, the software now also attempts to associate the device with the previous connection using its unique serial number, ensuring a smooth workflow despite the path change.
Disk imaging can now also be much more productive in scenarios involving damaged media. A new feature allows users to reset defective blocks back to "unread" status, enabling re-reading of previously skipped sections of the disk. This provides an opportunity to salvage more important data that may have been considered irretrievable during prior attempts to image those damaged areas.
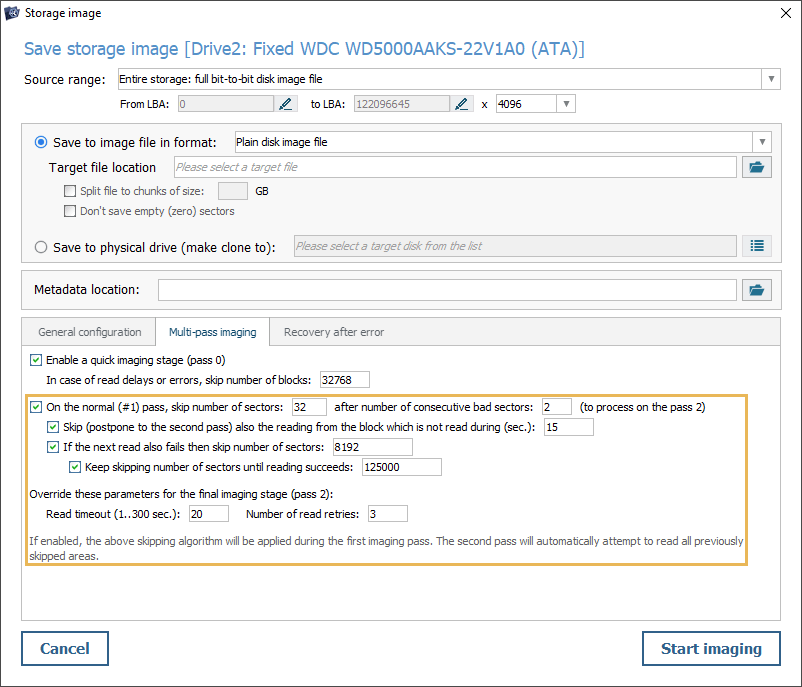
Moreover, UFS Explorer can now read sector maps created by DFL-DE, a disk imaging tool commonly used in professional settings. Such maps provide detailed information on each sector on the disk and its condition, which is absolutely necessary when working with faulty storage devices. The software supports both plain and optimized "compact" map formats, as well as log files produced during the imaging process. It is also capable of processing log files generated by certain third-party disk imaging solutions.
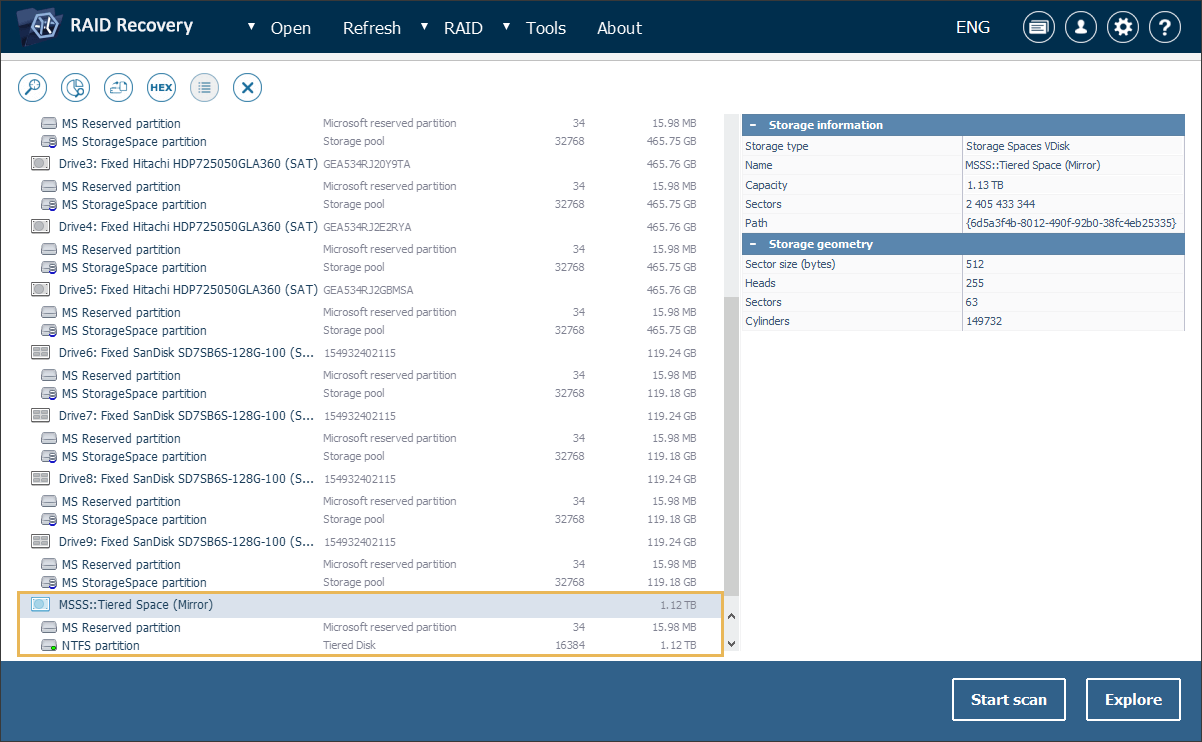
Support for multi-tier Microsoft Storage Spaces
The updated software editions are capable of working with more complex Microsoft Storage Spaces setups – ones that utilize multi-tier volumes. Such volumes comprise two types of storage media (e.g., SSDs and HDDs) within the same pool and move the data between the tiers in order to achieve better speed and improve storage capacity organization. At the same time, rotation groups may be used to distribute (rotate) that data between the drives for redundancy and performance. UFS Explorer allows users to access and recover files from this advanced configuration, in addition to the previously supported simple (stripe), mirror and parity volumes, now serving as an all-in-one solution for Microsoft Storage Spaces recovery.
More supported Apple’s virtual formats
Contemporary UFS Explorer utilities are able to open and process "directory-bundled" disk images of macOS straight from the local file system. Such formats like "sparsebundle" and "backupbundle" arrange files as packages of multiple smaller "bands" and are widely used for mac disk images and in Time Machine backups. Furthermore, Parallels Desktop virtualization software can create HDD bundles, virtual disks presented as directories containing multiple files, rather than individual large files. HDD bundles may also include separate files for snapshots that capture the state of the virtual machine at a specific moment in time. Automatic handling of those snapshots by UFS Explorer makes it much easier to restore specific states of Parallels virtual machines. And, in general, in view of the support for all these formats, the software becomes even more usable for Apple data recovery, providing more possibilities to access and retrieve data from the macOS system.
Improvements for easier file and folder saving
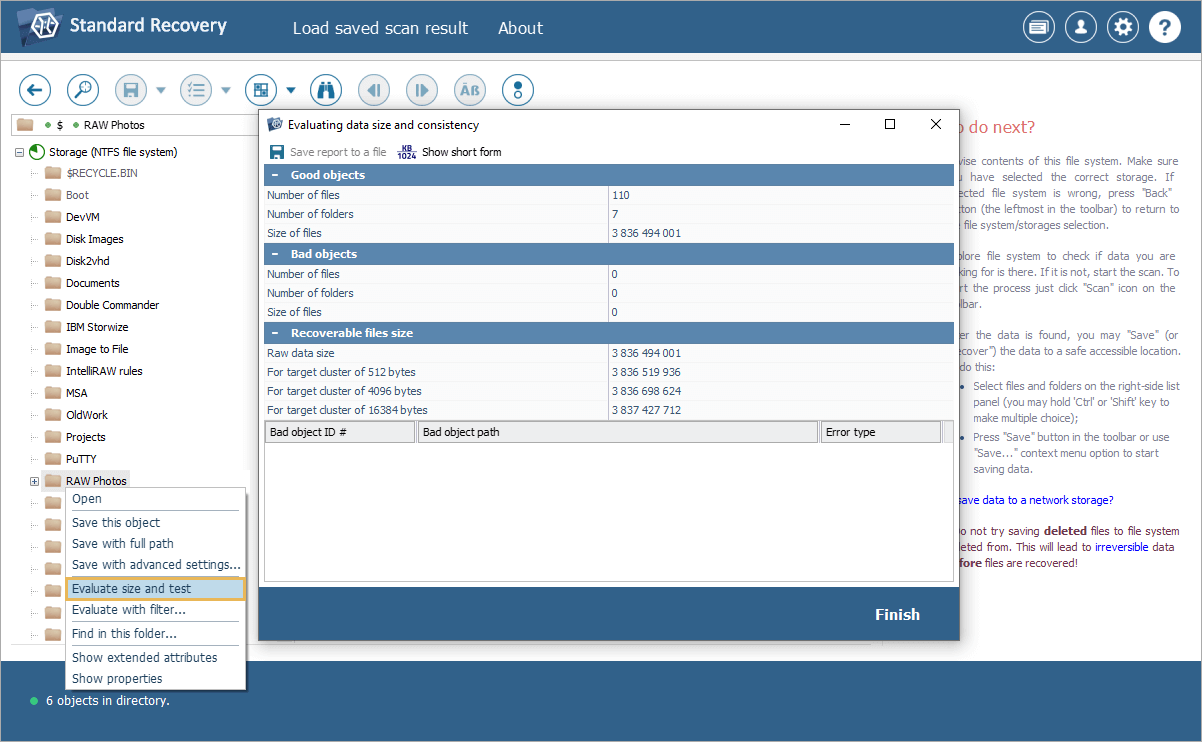
In the file system access mode, UFS Explorer can now calculate and display the size of subfolders and the number of files inside. This allows users to quickly estimate how much data is stored in each folder and how many files it contains, which may be handy when dealing with large volumes of content.
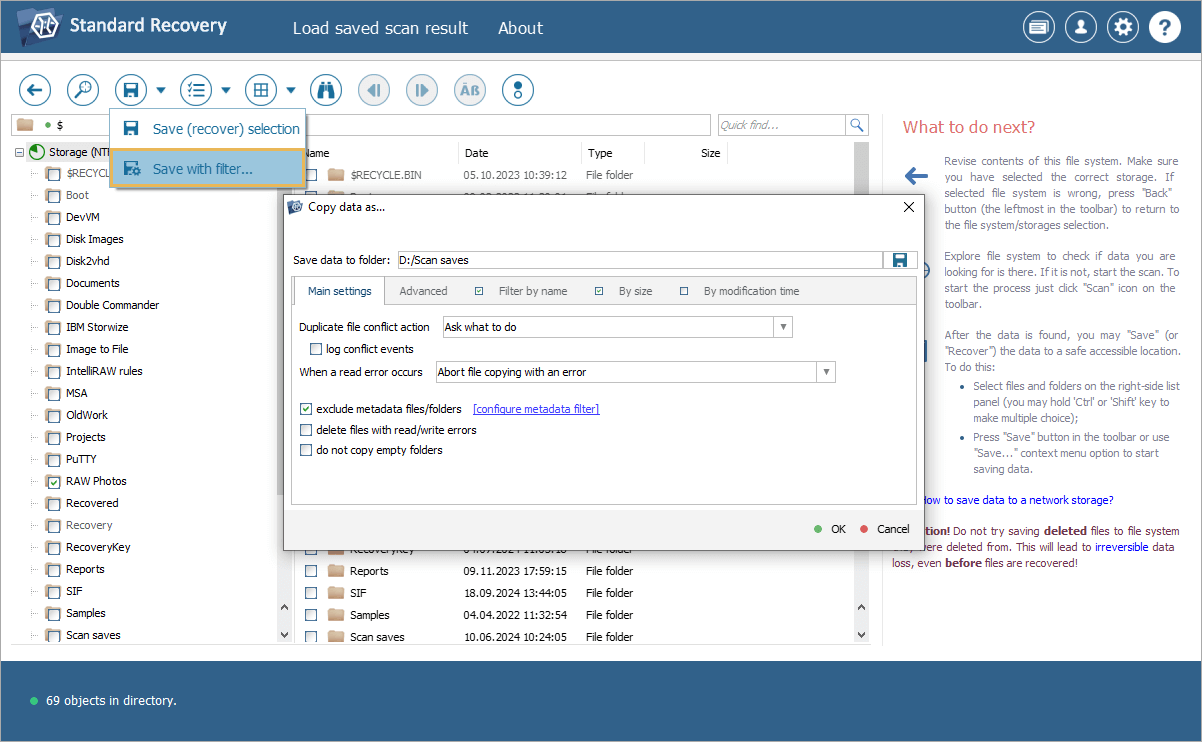
The interface for saving files with filters has also been reworked. The applicable filters are now separated into tabs, and it is possible to edit the target path for copying. Additionally, the mask for "folder exclusion" has been introduced as a separate setting for greater convenience.
UFS Explorer RAID Recovery, UFS Explorer Network RAID and higher
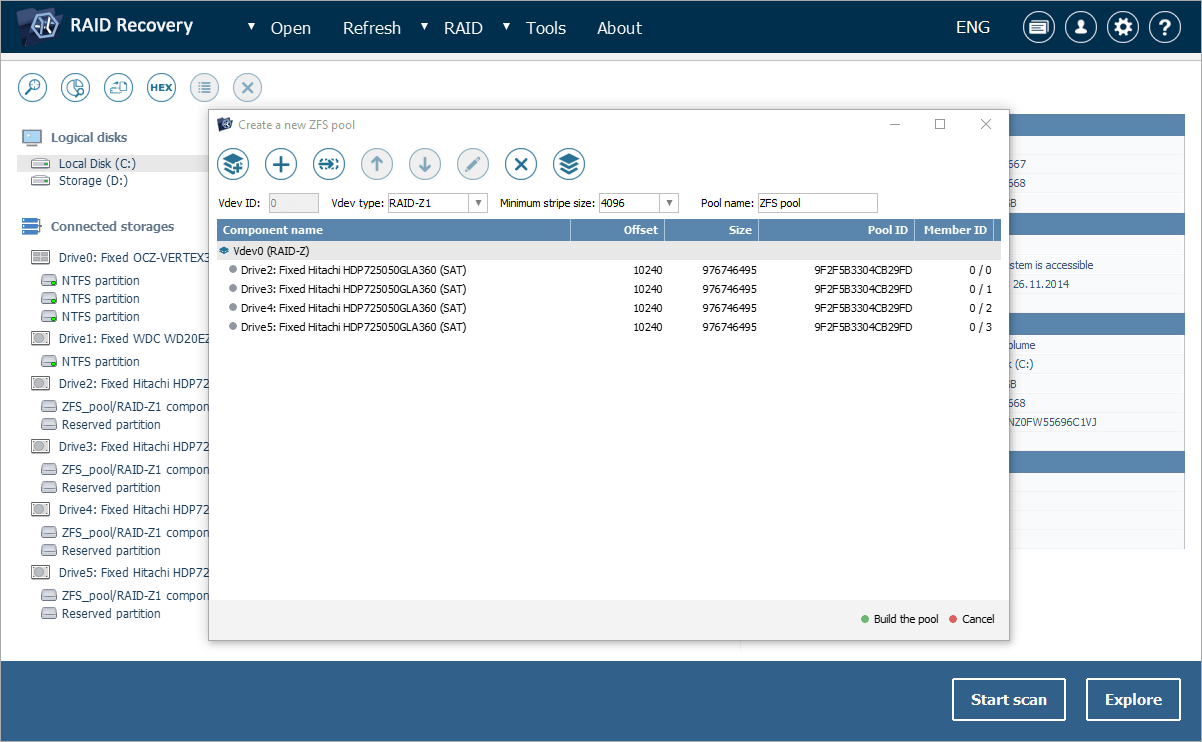
New ZFS pool builder tool
These more advanced editions of the software offer a dedicated GUI element for building and managing ZFS pools. It allows users to view and edit automatically reconstructed pools, modify such important pool properties as virtual devices (vdevs), their types, components and levels in case of RAID-Z. In addition, when certain components are missing or cannot be identified due to metadata corruption, placeholders can be assigned to their positions, ensuring that the pool structure remains readable. In situations where automatic pool assembly is not possible at all, the pool can be built from scratch by defining the respective configuration via the "RAID" menu. Such functionality is particularly useful in scenarios when existing pools are not detected correctly owing to partial damage and will otherwise be irrecoverable.
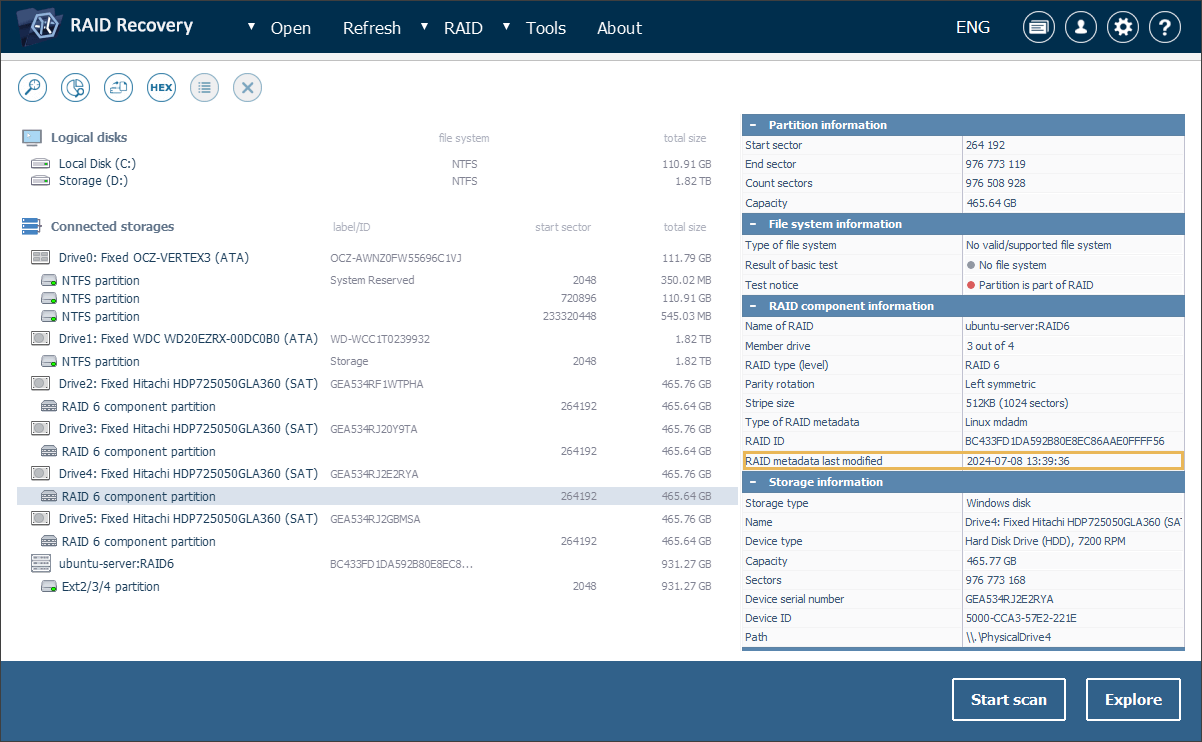
Broader range of supported RAID setups
The updated software has been equipped with more reliable RAID reconstruction algorithms, being able to cope with more scenarios of the array’s metadata damage. Together with that, when the "last updated" timestamp is available in the RAID metadata, its usage can help to select the most recent components when building the storage. The automatic inclusion of "incompletely rebuilt" components has also been disabled to ensure that only fully consistent ones are used, reducing the chances of inaccurate assembly.
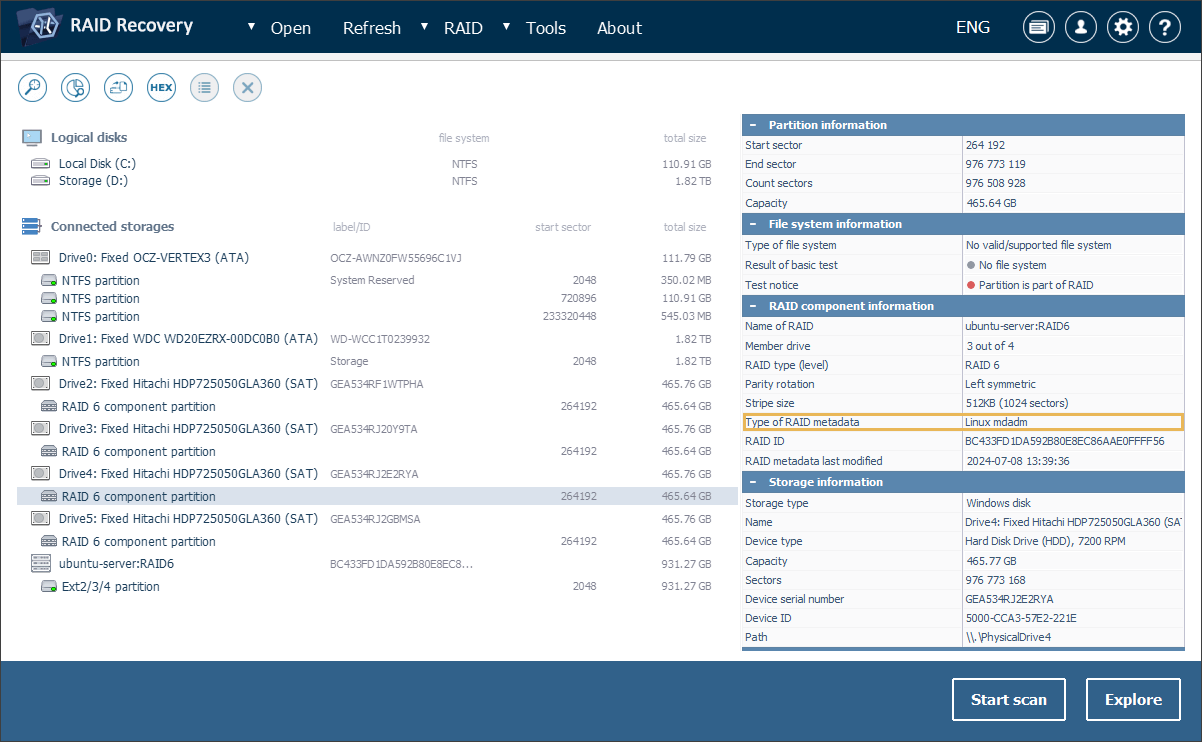
Presently, the programs also cover more mdadm RAID setups that have unusual parity configurations. The software can recognize RAID 5 and RAID 6 with dedicated parity ("parity first"/"parity last"), as well as RAID 6 arrays with RAID 5-style rotation and dedicated parity schemes, for example, "left-symmetric-6", "parity-first-6" and others. These variants are sometimes found in custom-built storage solutions and might be difficult to recover using traditional software tools. The possibility of automatic reconstruction of these configurations in UFS Explorer ensures that technical experts can effortlessly deal even with such highly specific storage systems.
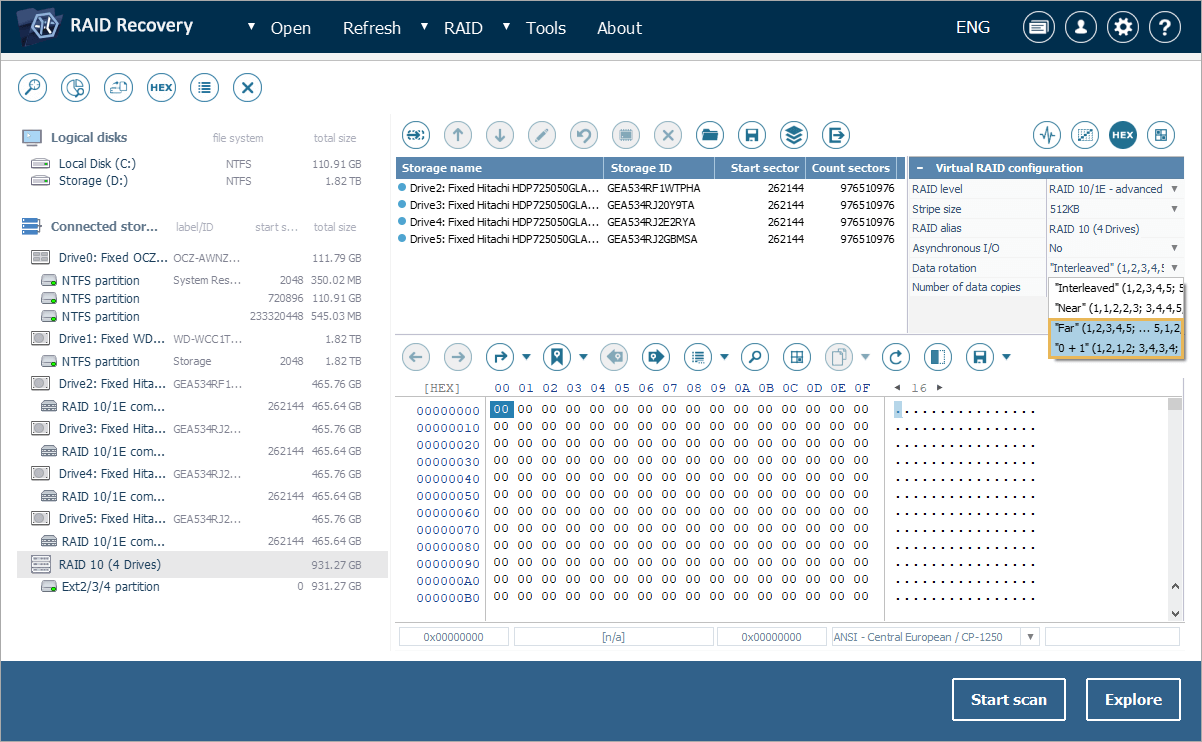
The support for RAID 10 and RAID 1E configurations has also been refined. The software is now able to work with multiple data copies in rotation, from two and up to the number of drives in the array. New rotation patterns like "Far" and "0+1" are also recognized alongside existing "Near" and "Interleaved" types (or "Offset"/"Near" in mdadm terminology).
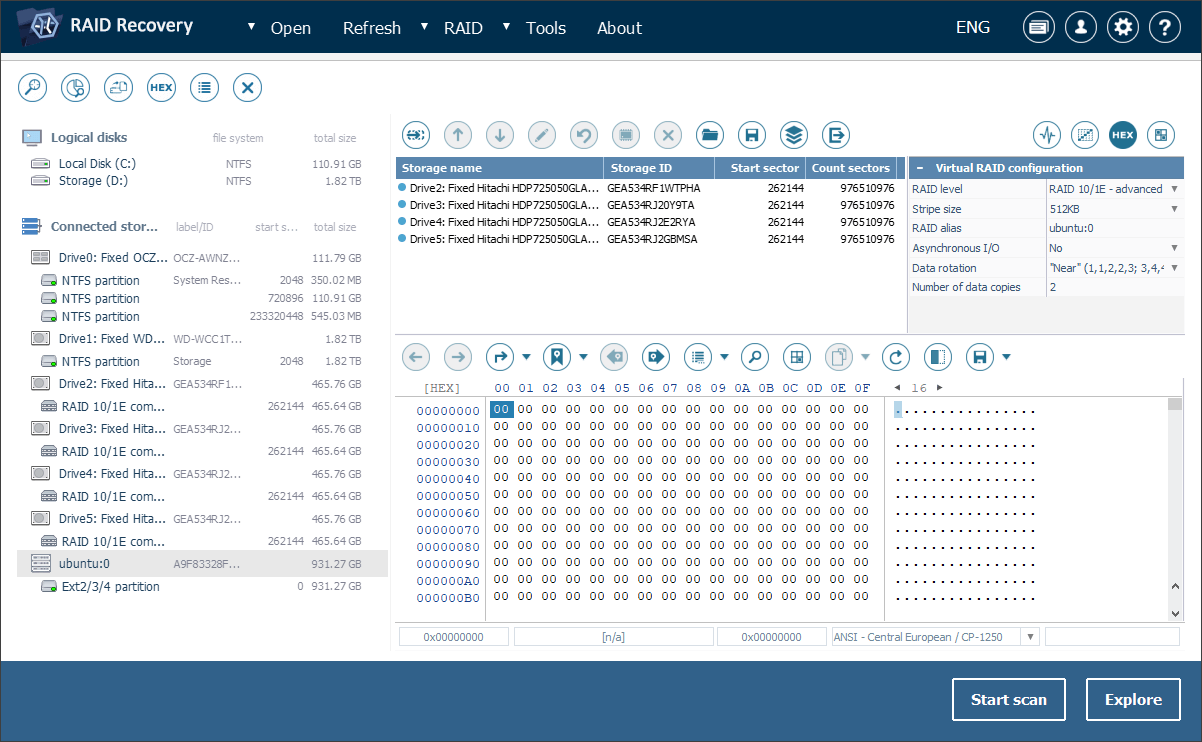
In addition, the utilities can now handle Softraid, a software-based implementation of RAID created in OpenBSD. This technology is quite popular in certain environments, but is not as widely supported as common RAID layouts. By allowing to work with RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5 and Span configurations of Softraid, UFS Explorer becomes an indispensable tool for users dealing with data loss within the OpenBSD infrastructure.
Expanded compatibility with Drobo
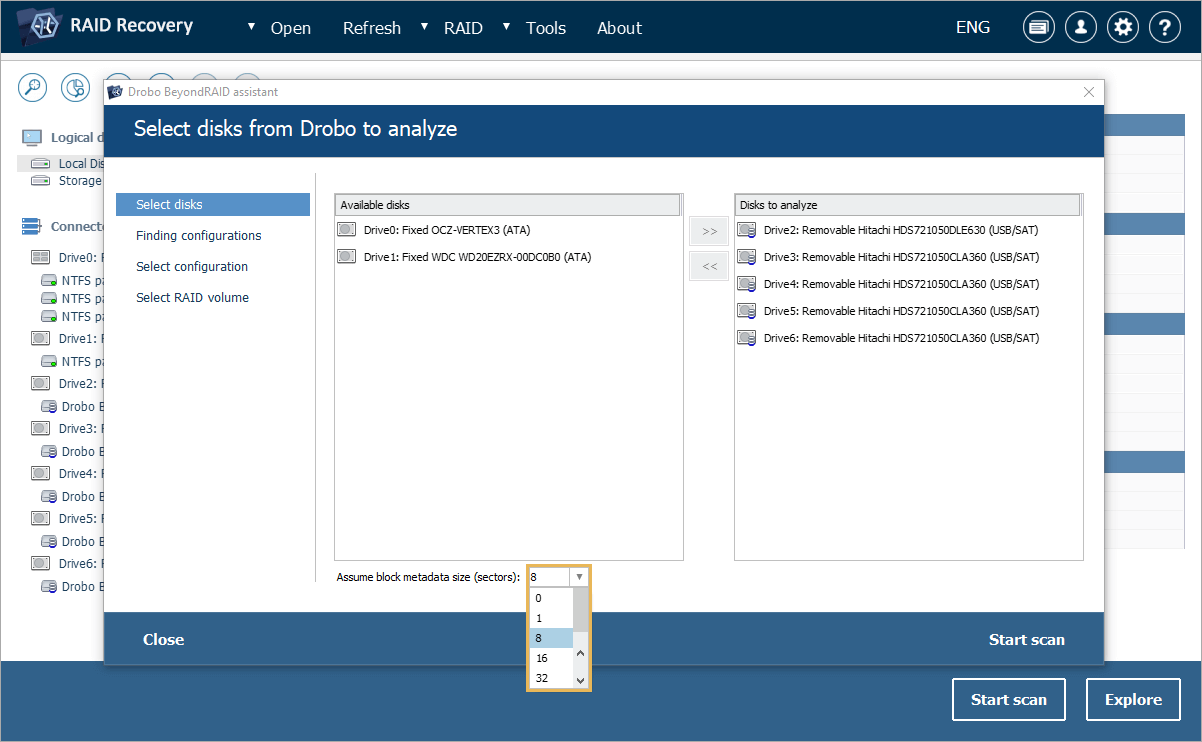
UFS Explorer has become even more adept at handling Drobo devices of various generations. The programs are able to interpret the "short-form" metadata encountered in the latest models of Drobo. Moreover, the Drobo assistant tool now allows users to specify the size of data block metadata manually, which is especially useful for supporting older Drobo appliances or firmware versions. These updates make the software well-applicable to both the latest and older Drobo storage solutions, ensuring smooth data recovery regardless of device age.
UFS Explorer Professional Recovery and higher
More recovery capabilities for Synology
Professional-grade UFS Explorer software has been updated to include support for Synology’s RAID-F1, a proprietary RAID layout designed specifically for their SSD-based storage systems. The programs can now identify, reconstruct and recover data from such Synology NAS setups, in addition to handling other RAID types, like Synology Hybrid RAID (SHR), RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6 and RAID 10. Furthermore, in scenarios where it is necessary to recover data from an encrypted volume, the ability to unwrap keys directly from Synology key vault files will simplify the decryption process for unimpeded access to the volume content.
Enhanced unlock and decryption features
The upgraded software has several important enhancements with regard to handling protected storage. First of all, it offers support for the ATA "security unlock" command. This makes it possible to unlock and access ATA hard drives and SSDs protected by the ATA security lock mechanism, as long as the correct user password is available (with the respective padding and transformation).
Secondly, UFS Explorer now allows users to recover data from OpenBSD softraid that employs password-based encryption. This way, such configurations can be processed in the software even when secured with a password, provided that the latter is provided correctly to the program.
And, finally, disks from WD MyBook devices equipped with the JMS561 bridge chip can now be decrypted using a simple double-click, which reduces the number of steps required to access encrypted data. Besides, span and stripe multi-disk RAID configurations on the decrypted storage will be recognized automatically.
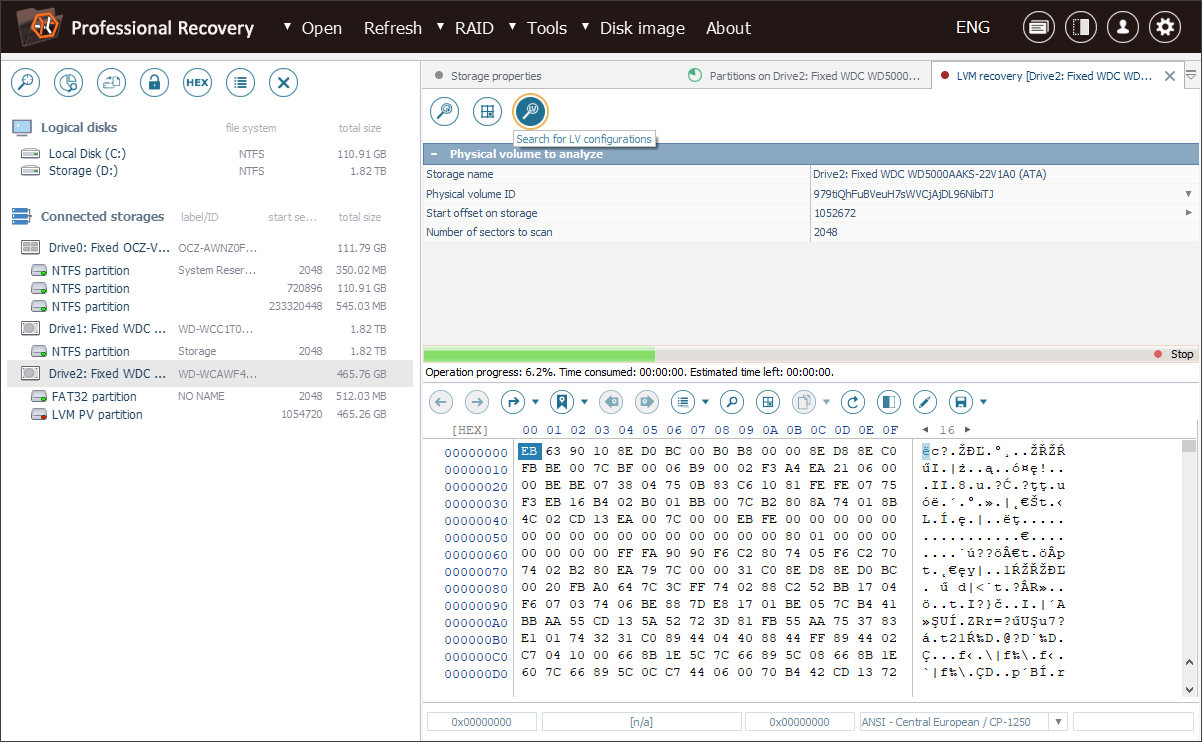
Better support for damaged LVM volumes
The updated utilities enable users to restore lost LVM setups even when the IDs of their physical volumes are unknown. Currently, it is possible to look for a missing or damaged LVM configuration through defining a physical volume, without having to specify its ID upfront. Such an approach allows searching for lost LVM metadata, but requires manual assignment of the storage components during the final stage of the recovery process.
Wider variety of supported proprietary RAID layouts
The professional-level editions of UFS Explorer have become more effective in dealing with various enterprise RAID setups. To begin with, the software now supports RAID 60 with Adaptec’s RAID 6 rotation, a non-conventional parity rotation scheme implemented by certain Adaptec RAID controllers. Secondly, it is now able to recognize arrays with 0+1-style rotation, an advanced configuration used in RAID 0+1 managed by HP's SmartArray controllers. And, lastly, it comes with support for two new RAID patterns based on the DDF metadata format – RAID 10 with "Far" rotation and RAID 00 rotation as a subvariant of RAID 0. The capability to handle these specific RAID configurations makes the software even more valuable for enterprise-grade data recovery.
Besides, when saving a RAID configuration built using "flat" disk images with a custom sector size, the programs now automatically preserve the sector size transformation within the saved configuration. This improvement removes the need to reapply these settings each time the configuration is loaded, ensuring accurate alignment of the RAID components and consitency of the array.
Extended support for Apple Core Storage volumes
Specialist-oriented UFS Explorer products now support another format of Apple Core Storage volumes, the ones utilizing "type 24 data allocation". The ability to understand this specific allocation scheme makes it possible for the software to reconstruct it correctly and thus recover data from a broader range of configurations used by older Apple devices relying on the HFS+ file system.
UFS Explorer Technician
The latest edition of UFS Explorer, released only last year, has introduced several significant updates that are exclusive to this very product.
Assortment of new plugins
The introduction of specialized data recovery plugins for UFS Explorer Technician significantly expands the software's functionality in respect of data recovery from Storage Area Networks. These plugins are designed precisely for SAN systems produced by a number of popular vendors and serve to automate the assembly of their storage pool configurations, providing straightforward access to the content of virtual volumes. Each plugin is tailored to specific SAN technologies, ensuring that users can smoothly work with the corresponding storage solutions and their unique configurations. The selection of new plugins currently includes ones for the following SAN products:
HP Enterprise Virtual Arrays (EVA)
HPE Modular Storage Arrays (MSA)
HPE 3PAR StoreServ
Dell PowerVault MD3 series, IBM DS3 series and NetApp E-series (aka Infiniti SAN)
IBM Storwize (V series).
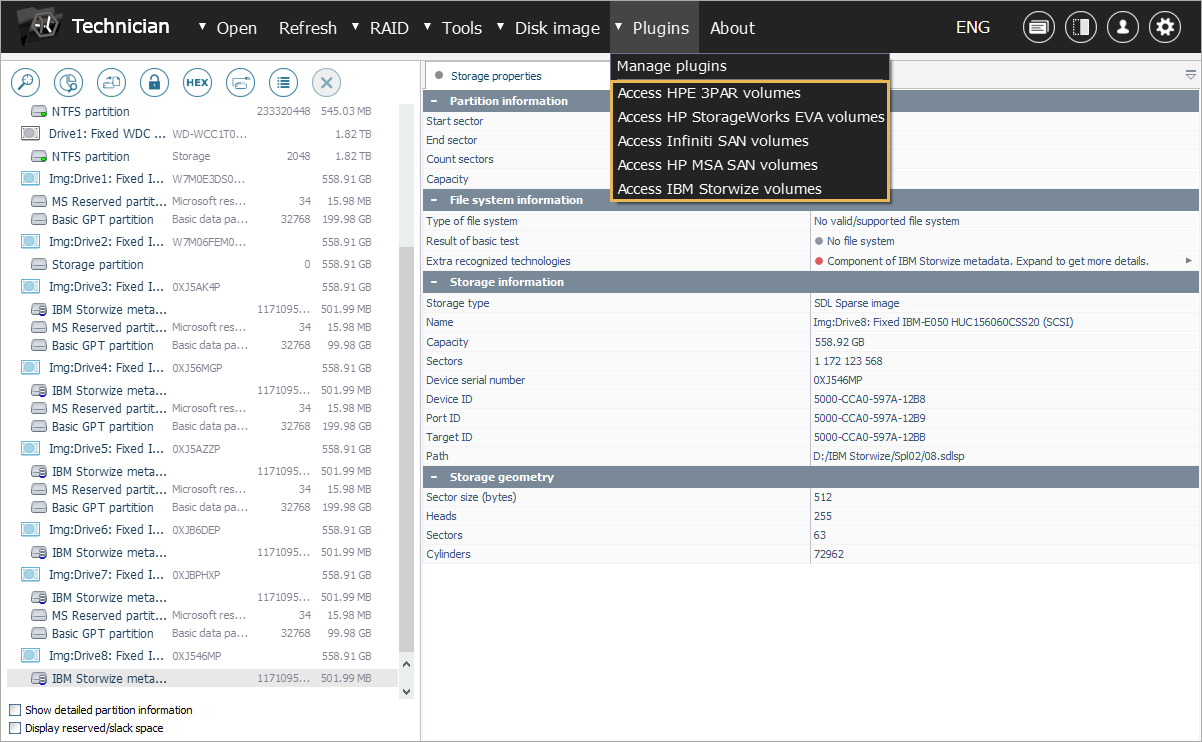
It is also important to mention that users can expect even more plugins in the future, broadening the range of supported storage solutions, or even create their own ones and integrate them into the program via a simple universal mechanism.
Support for QNAP QuTS Hero QZFS
The software has received support for the latest version QZFS, a variant of the ZFS file system developed by QNAP for their NAS devices. With QZFS support, UFS Explorer can effectively recover data from QNAP NAS running the QuTS hero operating system, besides a variety of other setups used by the appliances of this manufacturer.
On the whole, this overview illustrates the significant improvements in different editions of UFS Explorer, making an upgrade to their latest versions an appealing option. You can download the updated software via the prompts in the interface of the respective program or go directly to the Software Store, where you may also check a comprehensive log of all changes.
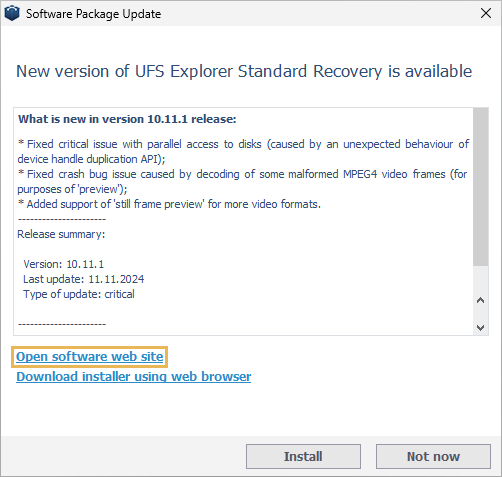
Difficulties in updating from version 10.7 and below
Due to a substantial change in the software update mechanism, users may encounter challenges when upgrading from UFS Explorer version 10.7 or earlier. Previously stored on the local server of SysDev Laboratories, the update files have now been migrated to Amazon Cloud. This service provides a more reliable infrastructure for hosting updates and helps to ensure higher download speeds worldwide. However, versions 10.7 and below are not compatible with the new protocol utilized by Amazon Cloud. As a result, the update process via the Software Manager and the in-software pop-up no longer functions for these older versions.
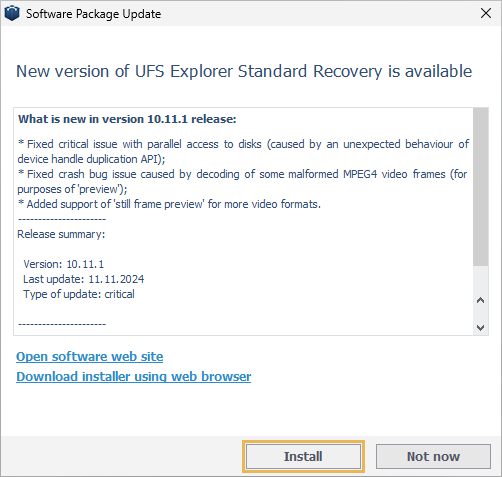
While attempting to update the software, users may also encounter an error message stating "Server of updates returned an error", which indicates a connection issue with the update server.
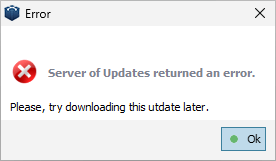
To resolve this, users with version 10.7 or earlier need to download the update manually from the UFS Explorer website. The "Open software website" button in the popup redirects to the product page, where the latest version of the software can be downloaded using the "Download" button.
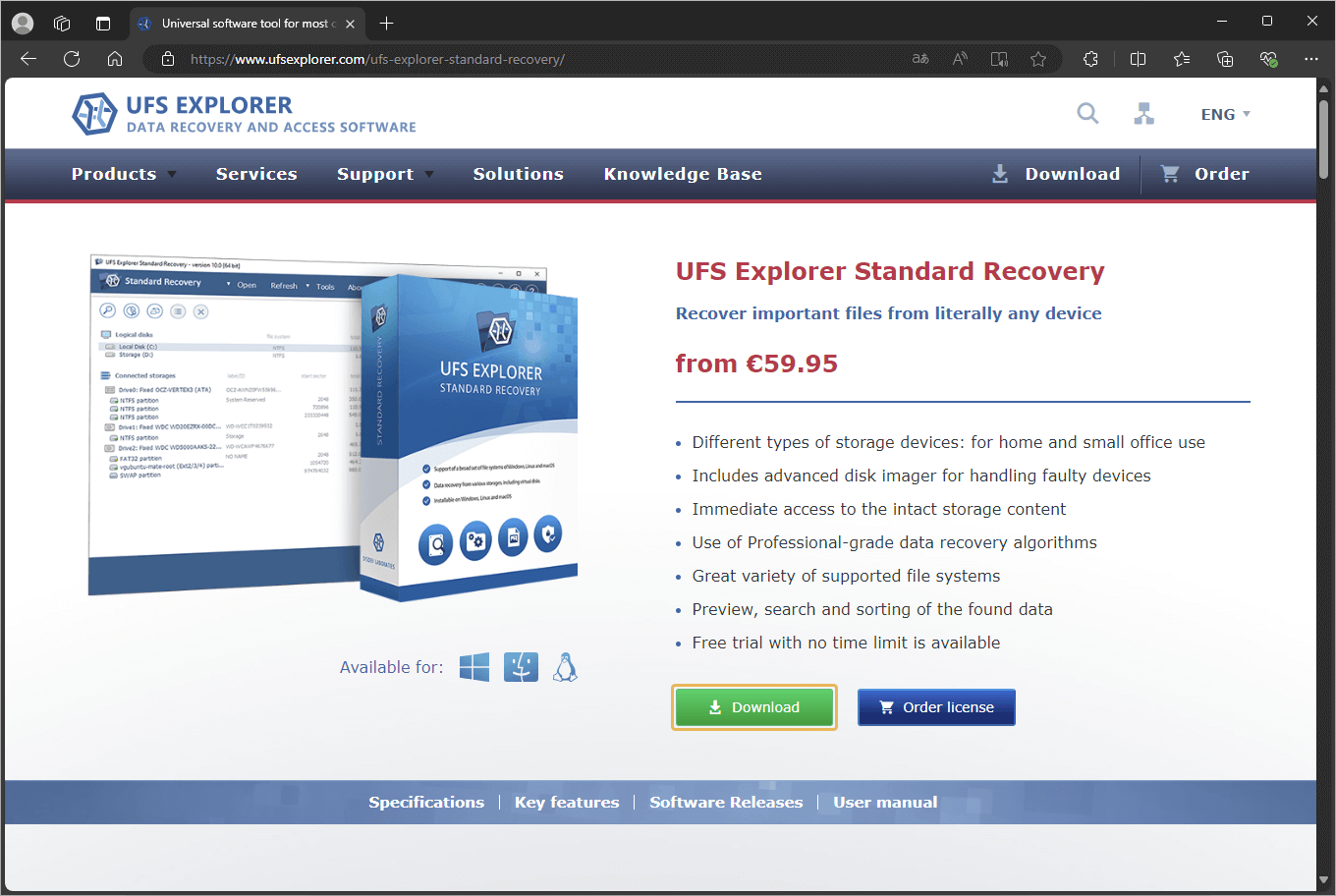
For users requiring an earlier version of UFS Explorer, such as version 10.10, the "Software Releases" section on the webpage provides access to previous software versions. From there, one may simply click the "Changes log" button and scroll down the page to locate the desired version.